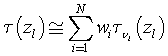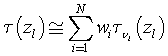Optimal Spectral Sampling (OSS) Description
The Optimal Spectral Sampling (OSS) method is a new rapid and
accurate technique developed at AER for the numerical modeling of
narrow band transmittances in media with non-homogeneous thermodynamic
properties containing a mixture of absorbing gases with variable
concentrations. The method has been specifically designed for the
modeling of radiances measured by Earth-orbiting down-looking microwave
and infrared radiometers, but can be applied to any spectral domain and
instrument viewing geometry. This technique can also be applied to the
general problem of flux or radiance computation in emitting and
scattering atmospheres. The OSS method is particularly well suited for
remote sensing applications and for the assimilation of satellite
observations in Numerical Weather Prediction models. Both applications
require fast and accurate models to produce radiances and Jacobians
used for the real-time inversion of multi-spectral satellite
observations. The OSS method is a generalized form of the exponential
sum fit technique, ESFT, and is equivalent to the ESFT technique in the
special case of a homogeneous atmosphere and a single constituent. The
OSS method approximates the atmospheric transmittance (or radiance) in
a given channel as a weighted sum of monochromatic transmittances (or
radiances) evaluated at selected wavenumbers (nodes) within the
interval spanned by the instrument function:
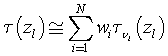
In the OSS approach, the wavelengths (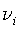 ) and weights (
) and weights (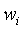 )are
obtained by minimizing the RMS difference between the exact and
estimated transmittance profiles (or radiances) for a set of training
profiles chosen to span the range of conditions to which the model will
be applied. The optimal selection of the
)are
obtained by minimizing the RMS difference between the exact and
estimated transmittance profiles (or radiances) for a set of training
profiles chosen to span the range of conditions to which the model will
be applied. The optimal selection of the 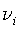 s is done using a Monte-Carlo search method applied to a set of uniformly spaced monochromatic transmittances,
s is done using a Monte-Carlo search method applied to a set of uniformly spaced monochromatic transmittances, 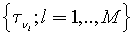 (or radiances) produced by a reference line-by-line model (e.g., LBLRTM) output.
(or radiances) produced by a reference line-by-line model (e.g., LBLRTM) output.
OSS attributes:
- OSS model parameters are derived for any instrument using
a fully automated and unsupervised search procedure (no manual tuning
is required).
- RT calculations are performed monochromatically from tabulated
optical depths for fixed and variable constituents, which provides an
accurate treatment of the surface reflection effects and significant
computational advantages over other existent RT parameterization
techniques used in remote sensing applications for the derivation of
the analytical Jacobians.
- The model accuracy can be improved by simply increasing the number of nodes
Atmospheric and Environmental Research